Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- family history of autoimmune thyroid disease
- history of tobacco use
- heat intolerance
- sweating
- weight loss
- palpitations
- tremor
- diffuse goiter
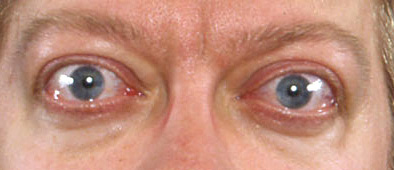
- orbitopathy
Other diagnostic factors
- irritability
- cardiac flow murmur
- moist, velvety skin
- scalp hair loss
- sexual dysfunction
- muscle weakness
- thyroid bruit
- onycholysis
- vitiligo
- pretibial myxedema
- acropachy
- menstrual irregularity
Risk factors
- family history autoimmune thyroid disease
- female gender
- tobacco use
- high iodine intake
- lithium therapy
- biologic agent and cytokine therapies
- radiation
- radioiodine therapy for benign nodular goiter
- stress
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
- serum free or total T4
- serum free or total T3
- TSH receptor antibodies (TRAb)
Tests to consider
- calculation of total T3/T4 or FT3/FT4 ratio
- radioactive iodine or technetium-99 uptake
- thyroid scan (scintigraphy)
- thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPOAb)
- thyroid ultrasound
- CT or MRI scan of orbit
- skin biopsy
Treatment algorithm
thyroid storm
subclinical Graves disease
symptomatic nonpregnant, nonlactating adults
pregnant women
children
Contributors
Authors
Salman Razvi, MD
Consultant Endocrinologist and Senior Lecturer
Translational and Clinical Research Institute, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead
Newcastle University
Newcastle upon Tyne
UK
Disclosures
SR has received speaker fees from Merck, IBSA, and Abbott Pharmaceuticals Ltd., all makers of levothyroxine. In addition, SR is in receipt of funding for an investigator-initiated trial from Merck to study the role of thyroid hormones in heart failure.
Acknowledgements
Dr Salman Razvi would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Petros Perros, Dr Douglas S. Ross, Dr George Hennemann, and Dr Vahab Fatourechi, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
PP, DSR, GH, and VF are authors of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Elizabeth N. Pearce, MD
Associate Professor of Medicine
Boston University Medical Center
Boston
MA
Disclosures
ENP is a consultant for Scientific Consulting Company GmbH and a management council member for the Iodine Global Network.
Kristien Boelaert, MD, PhD, FRCP
Reader in Endocrinology
Institute of Metabolism and Systems Research
College of Medical and Dental Sciences
University of Birmingham
Birmingham
UK
Disclosures
KB declares that she has no competing interests.
Paul Carroll, MD, FRCP
Clinical Lead for Endocrinology
Chair of Thyroid MDM
Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Trust
London
UK
Disclosures
PC declares that he has no competing interests.
David Cooper, MD
Division Head
Endocrinology
Sinai Hospital of Baltimore
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
DC declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Kahaly GJ, Bartalena L, Hegedüs L, et al. 2018 European Thyroid Association guideline for the management of Graves' hyperthyroidism. Eur Thyroid J. 2018 Jul 25;7(4):167-86.Full text Abstract
Ross DS, Burch HB, Cooper DS, et al. 2016 American Thyroid Association guidelines for diagnosis and management of hyperthyroidism and other causes of thyrotoxicosis. Thyroid. 2016 Oct;26(10):1343-421.Full text Abstract
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Thyroid disease: assessment and management. Oct 2023 [internet publication].Full text
Mooij CF, Cheetham TD, Verburg FA, et al. 2022 European Thyroid Association guideline for the management of pediatric Graves' disease. Eur Thyroid J. 2022 Jan 1;11(1):e210073.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Toxic nodular goiter
- Painless and postpartum thyroiditis
- Gestational hyperthyroidism
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Practice parameter for treatment of benign and malignant thyroid disease with I-131 sodium iodide
- 2022 European Thyroid Association guideline for the management of pediatric Graves' disease
More GuidelinesPatient information
Graves disease
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer