Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- dysmenorrhea
- menorrhagia
- enlarged, globular, tender uterus
- dyspareunia
- chronic pelvic pain
Other diagnostic factors
- subfertility or adverse pregnancy outcomes
- genitourinary or gastrointestinal pressure symptoms
Risk factors
- reproductive age group
- gravidity and parity
- early menarche
- endometriosis
- endometrial hyperplasia
- uterine leiomyoma
- black or Hispanic ethnicity
- short menstrual cycle
- spontaneous and induced abortion
- past uterine surgery
- use of tamoxifen
- obesity
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- ultrasound (US)
Investigations to consider
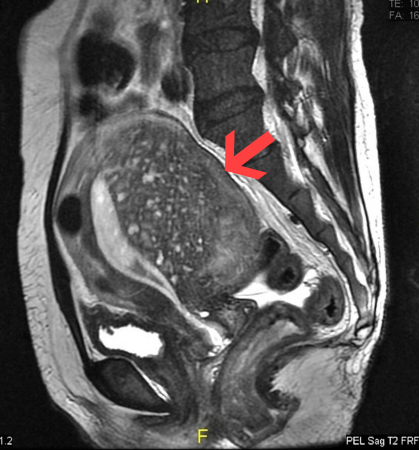
- MRI
- histologic diagnosis following hysterectomy
- hysterosalpingography (HSG)
Emerging tests
- fertility-sparing biopsy techniques
Treatment algorithm
future fertility desired
future fertility not desired
Contributors
Authors
Gaby Moawad, MD, FACOG
Clinical Associate Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology
The George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences
Washington
DC
Founder
The Center for Endometriosis & Advanced Pelvic Surgery (CEAPS)
McLean
VA
Disclosures
GM has received payment from Intuitive for speaking at conferences.
Youssef Youssef, MD, FACOG
Minimally Invasive Gynecology fellow
Maimonides Medical Center
Brooklyn
New York
NY
Disclosures
YY declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Elizabeth A. Stewart, MD
Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Consultant
Division of Reproductive Endocrinology
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Mayo Clinic
Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science
Rochester
MN
Disclosures
EAS has received grants for her institution from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality/Patient-Centered Outcome Research and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health; has received consulting fees from AbbVie and Anylyn; holds a patent for Methods and Compounds for Treatment of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding, which has no commercial activity; has received royalties from UpToDate; has received fees for developing educational content from the MED-IQ, Physicians' Education Resource, Omnia Education, Omnicuris, and WebMD; and serves as an unpaid advisor to The Fibroid Foundation and as unpaid treasurer of the International Gynecologic Society.
Meenu Priyadarshini Nanthakumar, MBBS, DNB(OG), MRCOG
ST6 Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Worcestershire Acute Hospitals NHS Trust
Worcestershire
UK
Disclosures
MPN declares that she has no competing interests.
Janesh Gupta, MSc, MD, FRCOG
Honorary Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Birmingham Women's and Children's Hospital
Birmingham
UK
Disclosures
JG declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Dason ES, Maxim M, Sanders A, et al; Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada (SOGC). Guideline no. 437: diagnosis and management of adenomyosis. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2023 Jun;45(6):417-29.e1.Full text Abstract
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Heavy menstrual bleeding: assessment and management. Mar 2018; updated May 2021 [internet publication].Full text
Munro MG, Critchley HOD, Fraser IS, et al. The two FIGO systems for normal and abnormal uterine bleeding symptoms and classification of causes of abnormal uterine bleeding in the reproductive years: 2018 revisions. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2018 Dec;143(3):393-408. Abstract
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists; Committee on Practice Bulletins - Gynecology. Practice bulletin no. 128: diagnosis of abnormal uterine bleeding in reproductive-aged women. Obstet Gynecol. 2012 Jul;120(1):197-206.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Leiomyomas (fibroids)
- Endometriosis
- Endometrial hyperplasia
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- SOGC guideline no. 437: diagnosis and management of adenomyosis
- ACOG practice bulletin no. 128: diagnosis of abnormal uterine bleeding in reproductive-aged women
More GuidelinesPatient information
Painful periods
Fertility problems: questions to ask your doctor
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer