Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
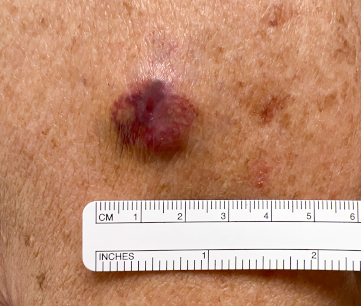
- firm, nontender, red or pink-to-violaceous or skin-colored papule or subcutaneous nodule
- rapidly growing lesion
Other diagnostic factors
- enlarged lymph nodes
- ulceration or bleeding cutaneous lesion
- small papules or nodules surrounding a primary lesion
Risk factors
- cumulative ultraviolet (UV) exposure
- immunosuppression
- advancing age
- male sex
- white skin
- Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV) infection with oncogenic transformation
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- biopsy and histopathologic assessment
- dermoscopy
Tests to consider
- lymph node ultrasound
- whole-body PET scan
- CT scan with contrast chest/abdomen/pelvis (± neck)
- brain MRI
- fine-needle aspiration or core biopsy
- sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB)
- Merkel cell polyomavirus serology
Emerging tests
- circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) analysis
Treatment algorithm
localized disease: stage I or II (T-any cN0 M0)
regional disease: stage IIIA
regional disease: unknown primary tumor with clinically apparent nodal disease
regional disease: stage IIIB
distant metastatic disease: stage IV
Contributors
Authors
Kelly Harms, MD, PhD
Associate Professor of Dermatology
Michigan Medicine
University of Michigan
Ann Arbor
MI
Disclosures
KH is a panel member for NCCN guidelines on Merkel cell carcinoma. She serves as Chair of Professionalism and Ethics for the Michigan Dermatological Society Board of Directors. KH is married to Paul Harms, a co-author of research on Merkel cell carcinoma.
Alison Lee, MD, MHS
Clinical Fellow
Department of Dermatology
Michigan Medicine
University of Michigan
Ann Arbor
MI
Disclosures
AL declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Isaac Brownell, MD, PhD
Senior Investigator
Dermatology Branch
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS)
National Institutes of Health (NIH)
Bethesda
MD
Disclosures
IB declares that he has no competing interests.
Zoe Venables, MbChB, MMedSci, MRCP
Clinical Associate Professor and Consultant Dermatologist
Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
Norwich
UK
Disclosures
ZV declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: Merkel cell carcinoma [internet publication].Full text
Gauci ML, Aristei C, Becker JC, et al; the European Dermatology Forum (EDF), the European Association of Dermato-Oncology (EADO), and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Diagnosis and treatment of Merkel cell carcinoma: European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline - update 2022. Eur J Cancer. 2022 Aug:171:203-31.Full text Abstract
Lugowska I, Becker JC, Ascierto PA, et al; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Merkel-cell carcinoma: ESMO-EURACAN clinical practice guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. ESMO Open. 2024 May;9(5):102977.Full text Abstract
Silk AW, Barker CA, Bhatia S, et al. Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) clinical practice guideline on immunotherapy for the treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancer. J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Jul;10(7):e004434.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
- Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the skin
- Amelanotic/hypomelanotic melanoma
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: Merkel cell carcinoma
- Merkel-cell carcinoma: ESMO-EURACAN clinical practice guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer