Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- sudden-onset (<72 hours) unilateral facial weakness
- ipsilateral severe ear/facial pain
- ipsilateral vesicular rash
- absence of constitutional symptoms
Other diagnostic factors
- dry eye
- vertigo
- hearing loss
- tinnitus
- epiphora
- altered taste
- oral lesions
- keratitis
Risk factors
- prior exposure to varicella zoster virus (VZV)
- age >50 years
- immunosuppression
- recent physiological stressor
- female sex
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- clinical diagnosis
- varicella zoster virus (VZV) polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Tests to consider
- electroneurography (evoked electromyography)
- MRI head and neck with contrast
- serology for Borrelia burgdorferi
Treatment algorithm
acute symptoms
chronic symptoms
Contributors
Authors
Jonas R. Miller, MD
Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Fellow Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery
UNC Facial Nerve Center
University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill
Chapel Hill
NC
Disclosures
JRM declares that he has no competing interests.
Matthew Q. Miller, MD
Assistant Professor Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
Director UNC Facial Nerve Center
University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill
Chapel Hill
NC
Disclosures
MQM is a paid consultant for Checkpoint Surgical, Inc.
Peer reviewers
Douglas J. Lanska, MD, MS, MSPH
Honorary Fellow
Department of Neurology
University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health
Madison
WI
Disclosures
DJL declares that he has no competing interests.
Mervi Kanerva, MD, PhD
Associate Professor
Senior ENT Consultant
Helsinki University Hospital
Helsinki
Finland
Disclosures
MK declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Gross GE, Eisert L, Doerr HW, et al. S2k guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2020 Jan;18(1):55-78.Full text Abstract
Jeon Y, Lee H. Ramsay Hunt syndrome. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2018 Dec;18(6):333-7.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
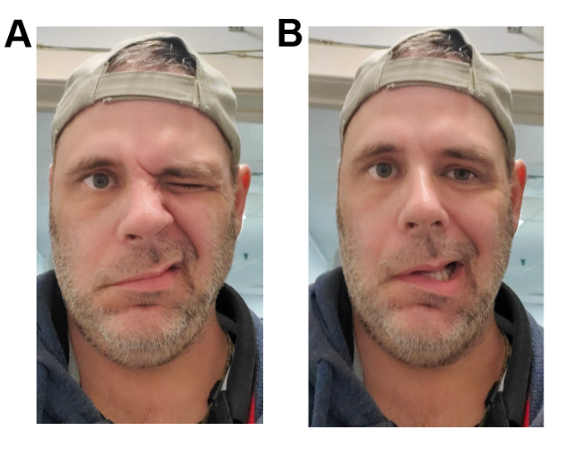
Differentials
- Bell’s palsy
- Malignant facial nerve tumor
- Benign facial nerve tumor (e.g., facial nerve schwannoma)
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- S2k guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer