Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- dyspnea
- productive cough
- fever
Other diagnostic factors
- chest pain
- asymmetric expansion of the chest
- diminished resonance
- egophony
- whisper pectoriloquy
- crackles or rhonchi
- tachycardia
- malaise/anorexia
Risk factors
- poor infection control/hand hygiene
- intubation and mechanical ventilation; endotracheal cuff pressure <20 cm H₂O
- supine position
- poor oral hygiene
- sedation/no interruption in sedation
- intubation/reintubation
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
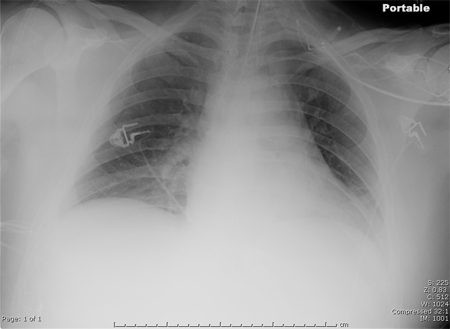
- chest x-ray
- WBC count with differential
- pulse oximetry
- culture of lower respiratory tract sample
Tests to consider
- ABG
- diagnostic thoracentesis
- CT chest
- CRP
- lung ultrasound
Emerging tests
- MRSA nasal swab
Treatment algorithm
before culture results: without risk factors for multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogen
before culture results: with risk factors for multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogen, including Pseudomonas and MRSA
after culture results: due to gram-negative pathogen
after culture results: due to gram-positive pathogen
Contributors
Expert advisers
Forest W. Arnold, DO, MSc, FIDSA
Professor of Medicine
Chief, Division of Infectious Diseases
Director Infectious Diseases Fellowship Training Program
Department of Medicine
School of Medicine
University of Louisville
Louisville
KY
Disclosures
FWA declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Krishna Sundar, MD, FCCP
Associate Professor (Clinical)
Department of Medicine
University of Utah
Director
Pulmonary and Critical Care Research
IHC Urban South
Utah Valley Pulmonary Clinic
UT
Disclosures
KS declares that he has no competing interests.
Ozan Akca, MD
Director of Research
Associate Professor
Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine
Neuroscience and Anesthesia Intensive Care Unit
University of Louisville
Louisville
KY
Disclosures
OA declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Kalil AC, Metersky ML, Klompas M, et al. Management of adults with hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia: 2016 clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society. Clin Infect Dis. 2016 Sep 1;63(5):e61-111.Full text Abstract
Klompas M, Branson R, Cawcutt K, et al. Strategies to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia, ventilator-associated events, and nonventilator hospital-acquired pneumonia in acute-care hospitals: 2022 Update. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2022 Jun;43(6):687-713.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- Cardiogenic pulmonary edema
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Strategies to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia, ventilator-associated events, and nonventilator hospital-acquired pneumonia in acute-care hospitals
- Management of adults with hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia
More GuidelinesVideos
Supraglottic airway devices: animated demonstration
Nasopharyngeal airway: animated demonstration
More videosPatient information
Pneumonia
更多 Patient information登录或订阅即可浏览 BMJ Best Practice 临床实践完整内容
内容使用需遵循免责声明