Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- food or stress triggers
- urinary urgency
- urinary frequency
- urinary incontinence
- nocturia
- dysuria
- pelvic-floor pain
- dyspareunia
- worsening of symptoms before menses
- urethral pain
- bladder neck pain
- suprapubic pain
- levator ani pain
- pain after placement of Foley catheter
Other diagnostic factors
- fibromyalgia
- vulvar vestibulitis
- vulvodynia
- features of systemic lupus erythematosus
- migraine
- features of rheumatoid arthritis
- features of chronic fatigue syndrome
- allergies
- sexual/domestic abuse
- scrotal or anal pain
Risk factors
- age 20 to 60 years
- female sex
- positive family history
- sexual or domestic abuse
- white ethnicity
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- urinalysis with microscopy and culture
- vaginal wet prep
- voiding diary
- urine cytology
Tests to consider
- cystoscopy with hydrodistention of bladder
- bladder biopsy
Emerging tests
- stress protein gene assay
- urine antiproliferative factor
- urine nerve growth factor (NGF)
Treatment algorithm
nonulcerative interstitial cystitis
ulcerative interstitial cystitis
Contributors
Authors
Kenneth M. Peters, MD
Professor and Chairman
Department of Urology
Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine
Chair
Department of Urology
Beaumont Health System
Royal Oak
MI
Disclosures
KMP declares that he has no competing interests.
Hailey Eisner, DO
Fellow, FPMRS Urology
Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine
Auburn Hills
MI
Disclosures
HE declares that she has no competing interests.
Priya Padmanabhan, MD, MPH
Professor of Urology
Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine
Auburn Hills
MI
Disclosures
PP declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Kenneth M. Peters, Dr Hailey Eisner, and Dr Priya Padmanabhan would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Lauren Tennyson, Dr Natalie Gaines, Dr Serge P. Marinkovic, Dr Robert Moldwin, Dr Stuart L. Stanton, Dr Lisa M. Gillen, Dr Christina Marinkovic, and Dr Michael Ehlert, the previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
LT, NG, SPM, RM, SLS, LMG, CM, and ME declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Nissrine Nakib, MD
Assistant Professor
Director of Female Urology and Urodynamics
University of Minnesota
Minneapolis
MN
Disclosures
NN declares that she has no competing interests.
Neil Baum, MD
Urologist
Touro Medical Office
New Orleans
LA
Disclosures
NB declares that he has no competing interests.
Charles Butrick, MD
Director
The Urogynecology Center
Overland Park
KS
Disclosures
CB declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Clemens JQ, Erickson DR, Varela NP et al. Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: AUA guideline amendment. J Urol. 2022 July;208(1):34-42.Full text
Engeler D, Baranowski AP, Berghmans B, et al. European Association of Urology. Guidelines on chronic pelvic pain. 2022 [internet publication].Full text
van de Merwe JP, Nordling J, Bouchelouche P, et al. Diagnostic criteria, classification, and nomenclature for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: an ESSIC proposal. Eur Urol. 2008 Jan;53(1):60-7. Abstract
Cox A, Golda N, Nadeau G, et al. CUA guideline: diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Can Urol Assoc J. 2016 May-Jun;10(5-6):E136-55.Full text Abstract
Imamura M, Scott NW, Wallace SA, et al. Interventions for treating people with symptoms of bladder pain syndrome: a network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 30;7(7):CD013325.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
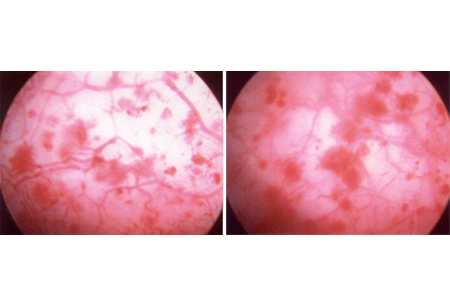
Differentials
- Endometriosis
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Urinary tract infection
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome
- Chronic pelvic pain
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer