Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
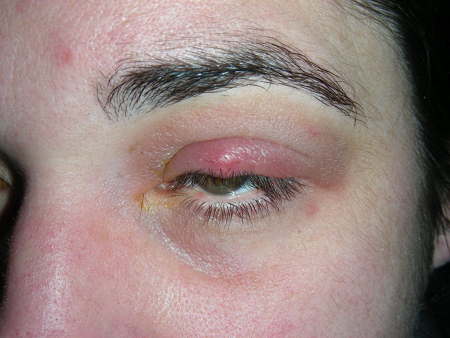
- acute pain of eyelid only
- pustule at eyelid margin
- pustule at tarsal conjunctiva
- palpable nontender nodule
- lack of constitutional symptoms
- lack of eye pain
- lack of intraocular pathology
Other diagnostic factors
- chronic swelling of eyelid
- age 30-50 years
- history of blepharitis and ocular rosacea
- astigmatism and blurred vision
Risk factors
- age 30-50 years
- blepharitis and ocular rosacea
- seborrheic dermatitis
- elevated serum cholesterol
- diabetes mellitus
- poor eyelid hygiene
- ethnic origin
- tuberculosis
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- clinical diagnosis
Tests to consider
- biopsy
- CT scan of face and orbits
Treatment algorithm
stye
chalazion
Contributors
Authors
Christopher McStay, MD

Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine
Vice Chair of Clinical Operations
Department of Emergency Medicine
Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons
New York
NY
Disclosures
CM declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Nickisa Hodgson, MD, MAS
Assistant Professor
Oculoplastic Surgery
Downstate Medical Center
Brooklyn
NY
Disclosures
NH declares that he has no competing interests.
Gus Gazzard, MA, MBBChir, MD, FRCOphth
Consultant Ophthalmic Surgeon
King's College Hospital
Honorary Research Fellow
Institute of Ophthalmology
London
UK
Disclosures
GG declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
The College of Optometrists. Clinical management guidelines: hordeolum. Feb 2023 [internet publication].Full text
Carlisle RT, Digiovanni J. Differential diagnosis of the swollen red eyelid. Am Fam Physician. 2015 Jul 15;92(2):106-12.Full text Abstract
Gordon AA, Danek DJ, Phelps PO. Common inflammatory and infectious conditions of the eyelid. Dis Mon. 2020 Oct;66(10):101042. Abstract
The College of Optometrists. Clinical management guidelines: chalazion (meibomian cyst). Feb 2023 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Blepharitis
- Dacryocystitis
- Dacryoadenitis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Clinical management guidelines: chalazion (meibomian cyst)
- Clinical management guidelines: hordeolum (stye)
More GuidelinesPatient information
Conjunctivitis
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer