Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- vertigo
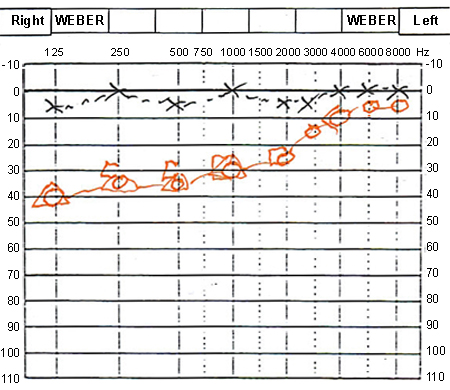
- hearing loss
- tinnitus
- aural fullness
- drop attacks
Other diagnostic factors
- positive Romberg test
- Fukuda stepping test
- bilateral symptoms
- nystagmus
- tandem walk
Risk factors
- recent viral infection
- genetic predisposition
- autoimmune disease
- increasing age
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- pure-tone air and bone conduction with masking
- speech audiometry
- tympanometry/immittance/stapedial reflex levels
- otoacoustic emissions (OAE)
Investigations to consider
- electrocochleography
- electronystagmography
- rotary chair test
- vestibular-evoked myogenic potential (VEMP)
- MRI of internal auditory canals
- thyroid function tests
- Lyme disease and syphilis serology
- antinuclear antibody
- antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody
- rheumatoid factor
Emerging tests
- 3-dimensional MRI
Treatment algorithm
all patients
persistent hearing loss
failure of medical and intratympanic therapies; hearing adequate
failure of medical and intratympanic therapies; hearing severely impaired
Contributors
Authors
Soha N. Ghossaini, MD, FACS

Otology-Neurotology
Ear Nose and Throat Associates of New York
New York
NY
Disclosures
SNG declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Ghossaini would like to gratefully acknowledge the late Professor Maurice H. Miller, a previous contributor to this topic. MHM declared that he had no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Steven D. Rauch, MD
Associate Professor of Otology and Laryngology
Harvard Medical School
Boston
MA
Disclosures
SDR declares that he has no competing interests.
Christopher J. Linstrom, MD
Professor
Otolaryngology/Head and Neck Surgery
The New York Eye and Ear Infirmary
Surgeon Director
New York
NY
Disclosures
CJL declares that he has no competing interests.
Peter Rea, MA, BM BCh, FRCS(ORL-HNS)
Consultant ENT Surgeon
Leicester Royal Infirmary
Leicester
UK
Disclosures
PR declares that he has no competing interests.
Doris Eva Bamiou, MD, MSc, PhD
Clinical Senior Lecturer & Consultant in Audiovestibular Medicine
Ear Institute
University College London
London
UK
Disclosures
DEB declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Goebel JA. 2015 Equilibrium Committee amendment to the 1995 AAO-HNS guidelines for the definition of Ménière's disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016 Mar;154(3):403-4. Abstract
Basura GJ, Adams ME, Monfared A, et al. Clinical practice guideline: Ménière's disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Apr;162(suppl 2):S1-55.Full text Abstract
Lopez-Escamez JA, Carey J, Chung WH, et al; Classification Committee of the Barany Society; Japan Society for Equilibrium Research; European Academy of Otology and Neurotology (EAONO); Equilibrium Committee of the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS); Korean Balance Society. Diagnostic criteria for Menière's disease. J Vestib Res. 2015;25(1):1-7.Full text Abstract
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: hearing loss and/or vertigo. 2018 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Acoustic neuroma
- Vestibular migraine (also called migraine-associated dizziness and migraine-associated vertigo)
- Vestibular neuronitis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Clinical practice guideline: Ménière's disease
- Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss (update)
More GuidelinesPatient information
Tinnitus
Meniere disease
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer