Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- dental pain/toothache
- thermal sensitivity of teeth
- fever
- intraoral and/or extraoral edema
- intraoral and/or extraoral erythema
- intraoral and/or extraoral discharge
- trismus
- tooth percussion sensitivity
- mobile teeth
- deep periodontal pockets, bleeding, gingival recession
- bone loss around teeth
- elevated/extruded tooth
- tachypnea
- dysphagia/drooling
- dysphonia
- dyspnea/respiratory stridor
- posturing
- uvular deviation
- floor of mouth elevation
- hypotension
Other diagnostic factors
- halitosis/bad taste in mouth
- xerostomia
- neurologic signs
Risk factors
- poor oral hygiene
- dental caries
- periodontal disease
- partially erupted or impacted tooth
- dental trauma
- fractured teeth
- excessive occlusal wear
- alcohol or drug misuse
- low socioeconomic status
- malnutrition
- age extremes
- prior radiation therapy
- certain medications
- immunosuppression or comorbidity (higher risk for complications)
- large dental restorations
- bruxism
- prior root canal treatment failure
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- CBC with differential
- panoramic radiograph
Tests to consider
- periapical radiograph
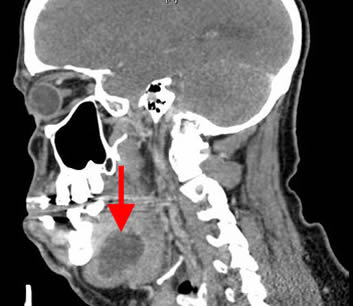
- CT head and neck (with contrast)
- infection site aspiration Gram stain/culture and sensitivity
- CRP
- ESR
- serum electrolytes
- plasma fibrinogen level
- MRI head and neck
- ultrasound of fascial spaces
- electric pulp testing
- thermal testing
- blood cultures
- C-terminal cross-linking telopeptide (CTX)
Treatment algorithm
high risk
low risk
Contributors
Authors
Melanie S. Lang, DDS, MD

Associate Professor
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
University of Washington School of Dentistry
Seattle
WA
Disclosures
MSL declares that she has no competing interests.
Thomas B. Dodson, DMD, MPH

Professor and Chair
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
University of Washington School of Dentistry
Seattle
WA
Disclosures
TBD is Editor-in-Chief for the Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. He is Chairperson for the Research and Development Commission of the AOCMF for which he receives reimbursement for travel and a per diem. TBD has received a National Institute of Health subaward for research in medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. He is a speaker for local and regional study clubs for which he receives honorarium. TBD is also an author of some references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Manish Kumar Bhagania, BDS, MDS
Clinical Associate Professor
Henry M Goldman School of Dental Medicine
Boston University
Boston
MA
Disclosures
MKB declares that he has no competing interests.
Kamran Ali, PhD, MMEd, BDS (Hons), FDSRCS, FCPS, FFDRCSI, FFDTEd, FDSRCPS, PFHEA
National Teaching Fellow
Professor
Faculty of Plymouth Health
University of Plymouth
Plymouth
UK
Disclosures
KA declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Lockhart PB, Tampi MP, Abt E, et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guideline on antibiotic use for the urgent management of pulpal- and periapical-related dental pain and intraoral swelling: a report from the American Dental Association. J Am Dent Assoc. 2019 Nov;150(11):906-21;e12.Full text Abstract
Cope AL, Francis N, Wood F, et al. Systemic antibiotics for symptomatic apical periodontitis and acute apical abscess in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Sep 27;9(9):CD010136.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Sinusitis
- Sialadenitis
- Mumps
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Antimicrobial prescribing in dentistry: good practice guidelines
- Evidence-based clinical practice guideline on antibiotic use for the urgent management of pulpal- and periapical-related dental pain and intraoral swelling: a report from the American Dental Association
More GuidelinesPatient information
Dental abscess: what is it?
Dental abscess: what are the treatment options?
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer