Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- asymptomatic
- cervical bruit
- focal neurologic deficit lasting >24 hours (i.e., stroke)
- focal neurologic deficit lasting <24 hours (i.e., transient ischemic attack [TIA])
Other diagnostic factors
- transient visual symptoms
Risk factors
- older age
- smoking
- history of cardiovascular disease
- history of hypertension
- history of hypercholesterolemia
- diabetes
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
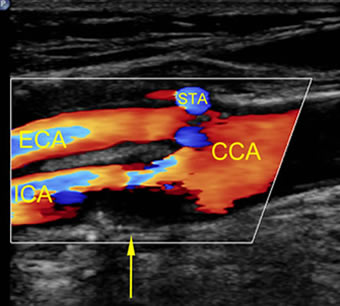
- duplex ultrasonography
- computed tomography angiography (CTA) of head, neck, and chest
Tests to consider
- magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) of head, neck, and chest
- CT brain
- MRI brain
Treatment algorithm
asymptomatic carotid stenosis <70%
asymptomatic carotid stenosis ≥70%: good surgical candidate
asymptomatic carotid stenosis ≥70%: poor surgical candidate
symptomatic
bilateral carotid stenosis
carotid restenosis
Contributors
Authors
Brajesh K. Lal, MD, FACS
Professor of Vascular Surgery
University of Maryland School of Medicine
Professor of Neurology
Mayo Clinic
Chief of the Vascular Service
Baltimore VA Medical Center
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
BKL declares that he has previously received a grant from the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA to conduct a multicenter study comparing revascularization to medical management for asymptomatic carotid stenosis.
Richard Bulbulia, MA, MD, FRCS
Associate Professor and Consultant Vascular Surgeon
Clinical Trial Service Unit and MRC Population Health Research Unit
Nuffield Department of Population Health
University of Oxford
Oxford
UK
Disclosures
RB declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Brajesh K Lal and Dr Richard Bulbulia would like to gratefully acknowledge Professor Martin M Brown, a previous contributor to this topic.
Peer reviewers
Tristan RA Lane, MBBS, BSc, PhD, FRCS
Consultant Vascular Surgeon
Cambridge Vascular Unit
Addenbrooke's Hospital
Cambridge University Hospital Trust
Cambridge
Honorary Senior Clinical Lecturer, Section of Vascular Surgery
Department of Surgery and Cancer
Imperial College London
UK
Disclosures
TRAL declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Brott TG, Halperin JL, Abbara S, et al. 2011 ASA/ACCF/AHA/AANN/AANS/ACR/ASNR/CNS/SAIP/SCAI/SIR/SNIS/SVM/SVS guideline on the management of patients with extracranial carotid and vertebral artery disease. Circulation. 2011 Jul 26;124(4):e54-130.Full text Abstract
Naylor R, Rantner B, Ancetti S, et al. Editor's choice - European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of atherosclerotic carotid and vertebral artery disease. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2023 Jan;65(1):7-111.Full text Abstract
AbuRahma AF, Avgerinos ED, Chang RW, et al. Society for Vascular Surgery clinical practice guidelines for management of extracranial cerebrovascular disease. J Vasc Surg. 2022 Jan;75(1s):4S-22S. Abstract
North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators. Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high-grade carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Aug 15;325(7):445-53.Full text Abstract
Grotta JC. Clinical practice. Carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2013 Sep 19;369(12):1143-50. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Carotid dissection or subintimal hematoma
- Thrombotic occlusion of the carotid artery resulting from plaque rupture
- Fibromuscular dysplasia
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2023 clinical practice guidelines on the management of atherosclerotic carotid and vertebral artery disease
- European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2023 clinical practice guidelines on the management of atherosclerotic carotid and vertebral artery disease
More GuidelinesPatient information
Carotid artery stenosis: what is it?
Carotid artery stenosis: what are the treatment options?
More Patient informationVideos
Carotid bruit
More videosLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer