Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- disk-shaped erythematous maculopapular scaly lesions
- age 20 to 40 years
- history of ultraviolet light exposure
- smoking history
Other diagnostic factors
- absence of pruritus and/or pain
- telangiectasia, hyperpigmentation, and/or hypopigmentation
- permanent scarring alopecia
- systemic features (arthritis, pleuritis, pericarditis, seizures, psychosis)
Risk factors
- age 20 to 40 years
- ultraviolet light exposure
- smoking
- female sex
- nonspecific skin injury
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- antinuclear antibodies, double-stranded (ds) DNA
- CBC
- ESR
- BUN and electrolytes
- urinalysis
Tests to consider
- skin biopsy
Treatment algorithm
nonsevere localized/limited disease
severe or refractory localized/limited disease; disseminated disease
Contributors
Authors
Meng May Chee, MBChB, MRCP
Consultant Rheumatologist
Wishaw General Hospital
Wishaw
UK
Disclosures
MMC declares that she has no competing interests.
Girish Gupta, MBChB, FRCP
Consultant Dermatologist
Lauriston Building
NHS Lothian
Edinburgh
UK
Disclosures
GG is an advisory board member of Almirall, Galderma, and Viatris. GG has also been reimbursed for consultancy work by Almirall, Galderma, and AbbVie, and has received honoraria from Almirall, Galderma, Viatris, and La Roche-Posay for giving lectures.
Acknowledgements
Dr Meng May Chee and Dr Girish Gupta would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Rajan Madhok, the previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
RM declared holding shares in GSK to the value of less than £12,000.
Peer reviewers
Jeffrey P. Callen, MD
Professor of Medicine (Dermatology)
University of Louisville
Louisville
KY
Disclosures
JPC declares that he has no competing interests.
Mark Goodfield, MD
Consultant Dermatologist
Department of Dermatology
Leeds General Infirmary
Leeds
UK
Disclosures
MG declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
O'Kane D, McCourt C, Meggitt S, et al; British Association of Dermatologists’ Clinical Standards Unit. British Association of Dermatologists guidelines for the management of people with cutaneous lupus erythematosus 2021. Br J Dermatol. 2021 Dec;185(6):1112-23.Full text Abstract
Lu Q, Long H, Chow S, et al. Guideline for the diagnosis, treatment and long-term management of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun. 2021 Sep;123:102707. Abstract
Kuhn A, Aberer E, Bata-Csörgő Z, et al. S2k guideline for treatment of cutaneous lupus erythematosus - guided by the European Dermatology Forum (EDF) in cooperation with the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017 Mar;31(3):389-404.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
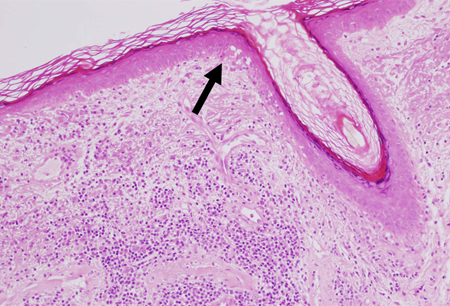
Differentials
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE)
- Psoriasis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Guideline for vaccinations in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases
- Guideline for the diagnosis, treatment and long-term management of cutaneous lupus erythematosus
More GuidelinesPatient information
Psoriasis: what is it?
Psoriasis: what are the treatment options?
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer