Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- nasal obstruction
- nasal discharge
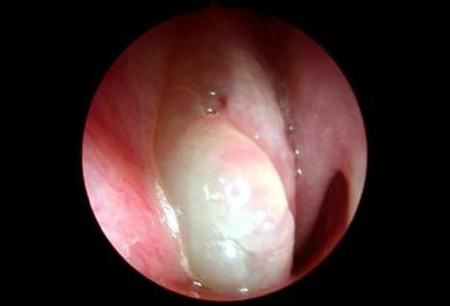
- polyps visible on examination or imaging
Other diagnostic factors
- facial pain/pressure
- reduced sense of smell/anosmia
- cough
Risk factors
- asthma
- eosinophilic granulomatous polyangiitis (EGPA, also known as Churg-Strauss syndrome)
- allergic fungal rhinosinusitis (AFRS)
- aspirin sensitivity
- genetic predisposition
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- anterior rhinoscopy
- nasal endoscopy
Tests to consider
- CT sinuses
- biopsy
- nasal smear and culture
- CBC with differential
- antineutrophil cytoplasm antibodies (ANCA)
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- skin prick tests/serum allergen-specific IgE tests
- aspirin challenge
- olfaction studies
- quality-of-life measures
- nasal airway assessment
Treatment algorithm
mild to moderate polyposis (VAS 0-7)
severe polyposis (VAS >7)
Contributors
Authors
Hesham A. Saleh, MBBCh, FRCS, FRCS (ORL-HNS)

Consultant Rhinologist
Charing Cross Hospital
Professor of Practice in Rhinology
Imperial College
London
UK
Disclosures
HAS declares that he has no competing interests.
Guy Scadding, FRCP, PhD
Consultant Allergist
Royal Brompton and Harefield NHS Trust
London
UK
Disclosures
GS has received lecture fees from ALK-Abello, Meda, and Glenmark Pharmaceuticals and sponsorship from GSK to attend a conference.
Acknowledgements
Dr Hesham A. Saleh and Dr Guy Scadding would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Richard J. D. Hewitt and Dr Romana Kuchai, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
RJDH and RK declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Sietze Reitsma, MD, PhD
Rhinologist
Amsterdam University Medical Centers
Amsterdam
Netherlands
Disclosures
SR declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2020. Rhinology. 2020 Feb 20;58(suppl s29):1-464. Abstract
Rank MA, Chu DK, Bognanni A, et al. The Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters GRADE guidelines for the medical management of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 Feb;151(2):386-98.Full text Abstract
Rimmer J, Fokkens W, Chong LY, et al. Surgical versus medical interventions for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(12):CD006991.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Nasopharyngeal cancer
- Congenital lesions (e.g., encephalocele, concha bullosa)
- Foreign body
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- The Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters GRADE guidelines for the medical management of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis
- European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2020
More GuidelinesVideos
How to examine the nasal cavity
More videosLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer