Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- small intestinal obstruction
- mucocutaneous pigmentation
Other diagnostic factors
- abdominal discomfort and distension
- abdominal pain
- gastrointestinal bleeding
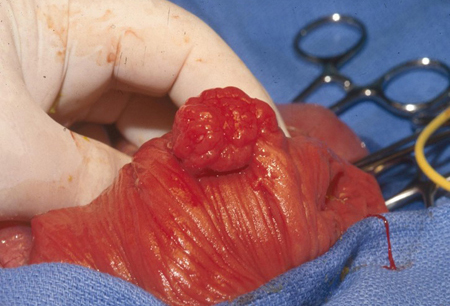
- polyp prolapse per anus
- enlarged testicles (without masses)
- bilateral gynecomastia
- fatigue
- pallor
Risk factors
- positive family history
- germline STK11 gene mutation
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- endoscopy
- magnetic resonance enterography
- polyp histology
- STK11 genetic testing
Treatment algorithm
initially confirmed polyposis: symptomatic or asymptomatic
following initial gastrointestinal surveillance
Contributors
Authors
Luke Engelking, MD
Associate Professor of Internal Medicine
UT Southwestern Medical Center
Dallas
TX
Disclosures
LE is a member of the Advisory Board for the Mayberry Memorial Foundation, a local nonprofit working to raise awareness of Lynch syndrome, for which he does not receive payment. He is the site Principal Investigator for a clinical trial in Familial adenomatous polyposis. He owns regular stock in Archer Daniels Midland, Howard Hughes Holdings and Target. He has previously owned regular stock in Merck & Co.
Acknowledgements
Dr Luke Engelking would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Thien An Mai Hoang’s contribution to this topic.
Dr Engelking would also like to acknowledge Dr Po-Hong Liu, Dr Brandie Heald, Dr James Church, and Dr Carol A. Burke, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
TAMH declares that she has no competing interests. BH declares that she has received payment from the following but has no contractual agreement to disseminate product information for them: Speakers Bureau Myriad Genetics Lab, and the advisory board for Invitae. BH is also President of the Collaborative Group of the Americas on Inherited Colorectal Cancer, for which she does not receive payment. CAB receives research support from Cancer Prevention Pharmaceuticals. PL and JC declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Suzanne MacFarland, MD, MTR
Assistant Professor of Pediatrics
University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine and Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
Philadelphia
PA
Disclosures
SM declares that she has no competing interests.
Patrick Morrison, MD
Consultant in Clinical Genetics
Department of Medical Genetics
Belfast HSC Trust
Belfast
UK
Disclosures
PM declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Syngal S, Brand RE, Church JM, et al; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: genetic testing and management of hereditary gastrointestinal cancer syndromes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb;110(2):223-62.Full text Abstract
Boland CR, Idos GE, Durno C, et al. Diagnosis and management of cancer risk in the gastrointestinal hamartomatous polyposis syndromes: recommendations from the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2022 Jun;162(7):2063-85.Full text Abstract
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: genetic/familial high-risk assessment: colorectal, endometrial, and gastric [internet publication].Full text
Monahan KJ, Bradshaw N, Dolwani S, et al. Guidelines for the management of hereditary colorectal cancer from the British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG)/Association of Coloproctology of Great Britain and Ireland (ACPGBI)/United Kingdom Cancer Genetics Group (UKCGG). Gut. 2020 Mar;69(3):411-44.Full text Abstract
Wagner A, Aretz S, Auranen A, et al. The management of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: European Hereditary Tumour Group (EHTG) guideline. J Clin Med. 2021 Jan 27;10(3):473.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Juvenile polyposis syndrome
- PTEN-hamartoma tumor syndrome
- Mixed hereditary polyposis syndrome
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: genetic/familial high-risk assessment: colorectal, endometrial, and gastric
- Pediatric cancer screening in hereditary gastrointestinal cancer risk syndromes: an update from the AACR Childhood Cancer Predisposition Working Group
More GuidelinesPatient information
Colon and rectal cancer: what is it?
Colon and rectal cancer: what are the treatment options?
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer