Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
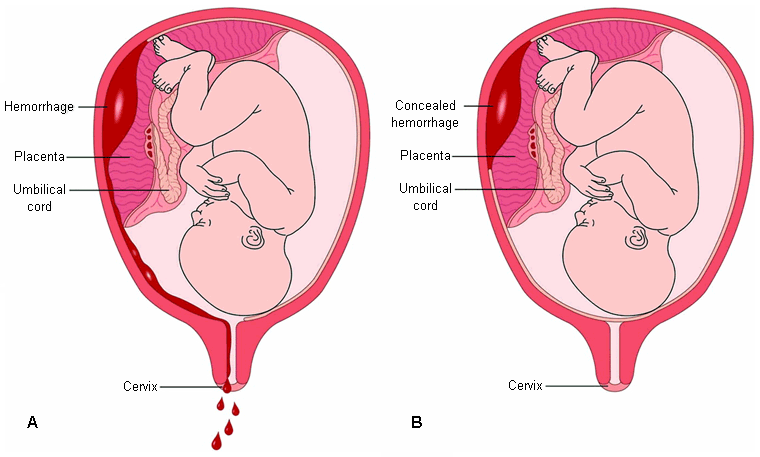
- vaginal bleeding
- abdominal pain
- uterine contractions
- uterine tenderness
Other diagnostic factors
- lower back pain
- fetal death
Risk factors
- chronic hypertension
- preeclampsia
- smoking
- cocaine use
- trauma
- prior cesarean delivery
- preterm premature rupture of the membranes
- multiparity
- advanced maternal age
- polyhydramnios
- chorioamnionitis
- uterine malformations
- prior placental abruption
- multifetal gestations
- oligohydramnios
- uterine leiomyomas
- thrombophilias
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- fetal monitoring
- Hb and hematocrit
- coagulation studies
- Kleihauer-Betke (K-B) test
- ultrasound
Tests to consider
- placental pathology
Treatment algorithm
all patients
live fetus: >34 weeks
live fetus: ≤34 weeks
fetal demise
Contributors
Authors
Yinka Oyelese, MD, FACOG

Director, Obstetric Imaging
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Harvard Medical School
Boston
MA
Disclosures
YO is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Anthony M. Vintzileos, MD, FACOG

Chairman
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Winthrop University Hospital
Mineola
Professor
Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Medicine
Stony Brook School of Medicine
Stony Brook
NY
Disclosures
AMV declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Christopher Glantz, MD, MPH
Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology
University of Rochester School of Medicine
Rochester
New York
NY
Disclosures
CG declares that he has no competing interests.
Austin Ugwumadu, PhD, FRCOG
Consultant/Senior Lecturer in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
St George's Hospital
London
UK
Disclosures
AU declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: second and third trimester bleeding. 2020 [internet publication].Full text
Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM), Gyamfi-Bannerman C. Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM) Consult Series #44: Management of bleeding in the late preterm period. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Jan;218(1):B2-8.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Preterm labor
- Placenta previa
- Chorioamnionitis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- ACR appropriateness criteria: second and third trimester vaginal bleeding
- Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM) Consult Series #44: Management of bleeding in the late preterm period
More GuidelinesPatient information
Appendicitis
Cystitis
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer