Summary
Differentials
Common
- Alcohol-related cerebellar degeneration
- Ischemic stroke (cerebellum)
- Ischemic stroke (brain stem)
- Hemorrhage in the cerebellum
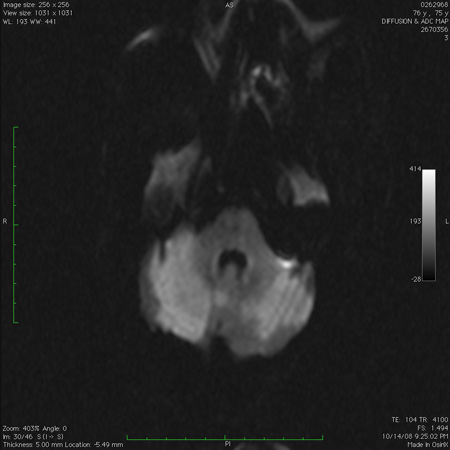
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
Uncommon
- Drug-induced ataxia
- Toxic neuropathies
- Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
- Sequel to hypoxic encephalopathy or heat stroke
- Acute cerebellitis
- HIV
- Gerstmann-Straussler syndrome
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob syndrome (CJD) (ataxic variant)
- Cerebellar abscess
- Whipple disease
- Neurosyphilis
- Posterior fossa tumors
- Craniovertebral junction anomalies
- Paraneoplastic sensory neuropathy
- Ataxia with anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) antibodies
- Celiac disease
- Myoclonus-opsoclonus syndrome
- Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration
- Miller-Fisher syndrome
- Sjogren syndrome
- Neuropathy related to monoclonal gammopathy
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Vitamin B1 deficiency
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Friedreich ataxia
- Ataxia telangiectasia
- Ataxia with oculomotor apraxia 1 (AOA1)
- Ataxia with oculomotor apraxia 2 (AOA2)
- Ataxia with vitamin E deficiency
- Abetalipoproteinemia
- Autosomal-recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay
- Ataxia due to POLG1 mutation
- Ataxia due to SCYL1 mutation
- Ataxia associated with CoQ10 deficiency
- Ataxia associated with metabolic errors
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 1 (SCA1)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 2 (SCA2)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 3 (SCA3)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 5 (SCA5)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 6 (SCA6)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 7 (SCA7)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 8 (SCA8)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 10 (SCA10)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 11 (SCA11)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 12 (SCA12)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 13 (SCA13)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 14 (SCA14)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 15/16 (SCA15/16)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 17 (SCA17)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 18 (SCA18)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 19/22 (SCA19/22)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 20 (SCA20)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 21 (SCA21)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 23 (SCA23)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 25 (SCA25)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 26 (SCA26)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 27 (SCA27)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 28 (SCA28)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 29 (SCA29)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 30 (SCA30)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 31 (SCA31)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 32 (SCA32)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 34 (SCA34)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 35 (SCA35)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 36 (SCA36)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 37 (SCA37)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 38 (SCA38)
- Spinocerebellar ataxia 40 (SCA40)
- Dentatorubral-pallido-luysian atrophy (DRPLA)
- Episodic ataxia type 1
- Episodic ataxia type 2
- Fragile-X tremor-ataxia syndrome (FXTAS)
- Mitochondrial cytopathy
- Niemann-Pick disease type C (NP-C)
Contributors
Authors
Vikram G Shakkottai, MD
Professor of Neurology
University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center
Dallas
TX
利益声明
VGS has research funding through the National Institutes of Health, and the National Ataxia Foundation. He serves as the Chair of the Scientific Advisory Board, National Ataxia Foundation and has received travel support for meetings organized by the National Ataxia Foundation. He is listed as an inventor on a patent (US-11382897-B2) filed by the University of Michigan for a therapeutic combination for cerebellar ataxia. He receives royalties from UptoDate Inc.
鸣谢
Professor Vikram G Shakkottai would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Barbara Kelly Changizi, Dr S.H. Subramony and Dr Hartmut Uschmann, previous contributors to this topic.
利益声明
SHS has received honoraria for lectures given from Athena Diagnostics Company. BKC and HU declare that they have no competing interests.
同行评议者
Camilla Kilbane, MD, FAAN
Center Director University Hospitals Cleveland Parkinson's and Movement Disorder Center
Associate Professor Neurology Case Western Reserve University
Cleveland
OH
利益声明
CK declares that she has done consulting work for Medtronic Inc. and Teva pharmaceuticals.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
参考文献
关键文献
Friedreich’s Ataxia Research Alliance. Clinical management guidelines for Friedreich ataxia: best practice in rare diseases. Nov 2022 [internet publication].全文 摘要
Ataxia UK. Management of the ataxias - towards best clinical practice (third edition). Jul 2016 [internet publication].全文
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: dizziness and ataxia. 2023 [internet publication].全文
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: ataxia - child. 2022 [internet publication].全文
参考文献
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
患者教育信息
Multiple sclerosis
Ovarian cancer
更多 患者教育信息登录或订阅即可浏览 BMJ Best Practice 临床实践完整内容
内容使用需遵循免责声明