Summary
Definition
History and exam
Other diagnostic factors
- previous nephrolithiasis
- flank pain
- hematuria
- costovertebral angle tenderness
- dysuria
- urinary urgency
- increased frequency of urination
- groin pain
Risk factors
- hemihypertrophy
- Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
- Caroli disease
- congenital hepatic fibrosis
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- family history of polycystic kidney disease
- chronic kidney disease
- hypercalciuria
- female sex
- hyperparathyroidism
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- urinalysis
- urine culture
- BUN and creatinine
- serum electrolytes
- abdominal radiography
- renal ultrasound
- intravenous urography
- noncontrast CT scan
- CT urogram
Investigations to consider
- 24-hour urine monitoring
- stone analysis
Treatment algorithm
with urinary tract infection (UTI)
with nephrolithiasis
Contributors
Authors
Michael J. Choi, MD
Associate Professor of Medicine
Clinical Director of Nephrology
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
MJC declares that he has no competing interests.
David S. Goldfarb, MD
Clinical Chief
Division of Nephrology
New York University School of Medicine
New York VA Medical Center
New York
NY
Disclosures
DSG is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Acknowledgements
Dr Michael J. Choi and Dr David S. Goldfarb would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Amaka Edeani, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
AE declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Khashayar Sakhaee, MD
Internal Medicine Physician
UT Southwestern Medical Center
Dallas
TX
Disclosures
KS declares that he has no competing interests.
Eric N. Taylor, MD, MSc
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Harvard Medical School
Renal Division
Brigham and Women's Hospital
Channing Laboratory
Boston
MA
Disclosures
ENT declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Forster JA, Taylor J, Browning AJ, et al. A review of the natural progression of medullary sponge kidney and a novel grading system based on intravenous urography findings. Urol Int. 2007;78(3):264-9. Abstract
Imam TH, Patail H, Patail H. Medullary sponge kidney: current perspectives. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2019;12:213-8.Full text Abstract
Gambaro G, Feltrin GP, Lupo A, et al. Medullary sponge kidney (Lenarduzzi-Cacchi-Ricci disease): a Padua Medical School discovery in the 1930s. Kidney Int. 2006 Feb;69(4):663-70. Abstract
Maw AM, Megibow AJ, Grasso M, et al. Diagnosis of medullary sponge kidney by computed tomographic urography. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007 Jul;50(1):146-50. Abstract
Pearle MS, Goldfarb DS, Assimos DG, et al; American Urological Association. Medical management of kidney stones: AUA guideline. J Urol. 2014 Aug(reviewed and validity confirmed 2019);192(2):316-24.Full text Abstract
Türk C, Neisius A, Petrik A, et al. EAU guidelines on urolithiasis. 2022 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
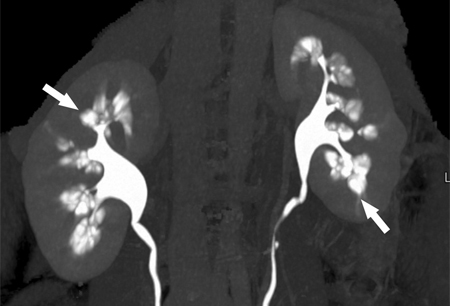
Differentials
- Distal renal tubular acidosis
- Renal papillary necrosis
- Tuberculosis of kidney
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Guidelines on urolithiasis
- Surgical management of stones: AUA/Endourological Society guideline
More GuidelinesPatient information
Kidney stones
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer