Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- history of famine or monotonous diet
- child <5 years of age and living in rural community
- low weight for height, low height for age, or a low mid-upper arm circumference (MUAC)
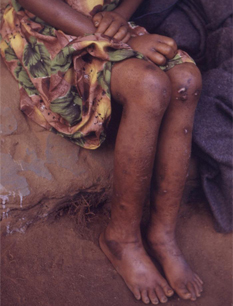
- bilateral pitting edema
Other diagnostic factors
- hair discoloration
- dermatosis/ulceration
- apathy and reluctance to feed
- hypothermia
- oral candida
- xerophthalmia
- pallor
- poor hydration
- fever
- irritability
Risk factors
- endemic food insecurity or famine
- rural communities
- <5 years of age
- monotonous diet based on maize or cassava
- dietary protein deficiency
- HIV infection
- tuberculosis (TB) nfection
- measles infection
- diarrhea
- weaning off the breast
- exposure to free radicals
- antioxidant deficiency
- aflatoxin poisoning
- incomplete immunization
- poor social or economic conditions
- cerebral palsy
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- clinical diagnosis
Tests to consider
- urine dipstick
- complete blood count (CBC)
- serum electrolytes
- serum protein
- serum albumin
- blood glucose
- chest x-ray (CXR)
- urine culture
- blood culture
- stool culture
- tuberculosis (TB) skin testing
- HIV serology/polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- malaria screen
- echocardiography
Treatment algorithm
uncomplicated
complicated
Contributors
Authors
Mark J. Manary, MD
Helene B. Roberson Professor of Pediatrics
Washington University School of Medicine
St Louis
MO
Disclosures
MJM is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Indi Trehan, MD, MPH, DTM&H
Associate Professor of Pediatrics
Adjunct Associate Professor of Global Health and Epidemiology
University of Washington
Seattle
WA
Disclosures
IT is the co-author of a reference cited in this topic.
Acknowledgements
Dr Mark J. Manary and Dr Indi Trehan would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr James E.G. Bunn, the previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
JEGB declared that he had no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Beatrice Amadi, MD, MMed.Paed
Consultant Paediatrician
University Teaching Hospital
Department of Paediatrics and Child Health
Lusaka
Zambia
Disclosures
BA declares that she has no competing interests.
Tahmeed Ahmed, MD
Adjunct Professor
Public Health Nutrition
James P. Grant School of Public Health
BRAC University
Dhaka
Bangladesh
Disclosures
TA declares that he has no competing interests.
George J. Fuchs III, MD
Professor of Pediatrics and Health Policy and Management
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
Little Rock
AR
Disclosures
GJF declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
World Health Organization. Management of severe malnutrition: a manual for physicians and other senior health workers. 1999. [internet publication].Full text
World Health Organization. Management of the child with a serious infection or severe malnutrition: guidelines for care at the first-referral level in developing countries. 2000. [internet publication].Full text
World Health Organization. WHO guideline on the prevention and management of wasting and nutritional oedema (acute malnutrition) in infants and children under 5 years. 2023 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Marasmus
- Chronic undernutrition
- Congestive heart failure
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- WHO guideline on the prevention and management of wasting and nutritional oedema (acute malnutrition) in infants and children under 5 years
- WHO child growth standards and the identification of severe acute malnutrition in infants and children
More Guidelines登录或订阅即可浏览 BMJ Best Practice 临床实践完整内容
内容使用需遵循免责声明