Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- inability to 'pop' or 'clear' the ear with changes in barometric pressure
- normal head and neck examination
Other diagnostic factors
- aural fullness
- subjective hearing loss
- autophony
- history of serous otitis media or of chronic otitis media
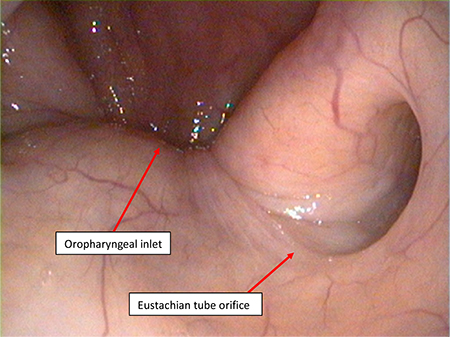
- oedema of the Eustachian tube orifice
- history of retracted or hypermobile tympanic membrane
Risk factors
- cleft palate
- adenoid hypertrophy
- allergic rhinitis
- chronic rhinosinusitis
- neoplasm of nasopharynx or infratemporal fossa
- Eustachian tube trauma
- Eustachian tube infection
- age <5 years
- cigarette smoking
- GORD
- radiation exposure
- history of recent weight loss
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- nasal endoscopy
- tympanometry
Investigations to consider
- nasopharyngoscopy
- CT scan
Treatment algorithm
all patients
Contributors
Authors
Edward D. McCoul, MD, MPH
Associate Professor
Department of Otorhinolaryngology
Ochsner Clinical School
University of Queensland School of Medicine
New Orleans
LA
Disclosures
EDM is the author of references cited in this topic and is a consultant for Stryker.
Acknowledgements
Dr Edward D. McCoul would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Erica R. Thaler, the previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
ERT declared that she had no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Alan G. Micco, MD
Associate Professor
Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery
Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine
Chicago
IL
გაფრთხილება:
AGM declares that he has no competing interests.
Niels van Heerbeek, MD, PhD
Consultant
Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery
University Medical Centre
Nijmegen
The Netherlands
გაფრთხილება:
NVH declares that he has no competing interests.
რეცენზენტების განცხადებები
BMJ Best Practice-ის თემების განახლება სხვადასხვა პერიოდულობით ხდება მტკიცებულებებისა და რეკომენდაციების განვითარების შესაბამისად. ქვემოთ ჩამოთვლილმა რეცენზენტებმა თემის არსებობის მანძილზე კონტენტს ერთხელ მაინც გადახედეს.
გაფრთხილება
რეცენზენტების აფილიაციები და გაფრთხილებები მოცემულია გადახედვის მომენტისთვის.
წყაროები
ძირითადი სტატიები
Bluestone CD. Eustachian tube: structure, function, role in otitis media. Hamilton, Ontario: BC Decker, Inc.; 2005.
Monsell EM, Harley RE. Eustachian tube dysfunction. Otolaryngol Clin N Am. 1996;29:437-444. აბსტრაქტი
Monsell EM, Harley RE. Eustachian tube dysfunction. Otolaryngol Clin N Am. 1996;29:437-444. აბსტრაქტი
Schilder AG, Bhutta MF, Butler CC, et al. Eustachian tube dysfunction: consensus statement on definition, types, clinical presentation and diagnosis. Clin Otolaryngol. 2015 Oct;40(5):407-11.სრული ტექსტი აბსტრაქტი
გამოყენებული სტატიები
ამ თემაში მოხსენიებული წყაროების სრული სია ხელმისაწვდომია მომხმარებლებისთვის, რომლებსაც აქვთ წვდომა BMJ Best Practice-ის ყველა ნაწილზე.
დიფერენციული დიაგნოზები
- Sensorineural hearing loss
მეტი დიფერენციული დიაგნოზებიგაიდლაინები
- Balloon dilation for chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction
- Balloon dilation of the Eustachian tube
მეტი გაიდლაინებიპაციენტის ბროშურები
Ear pain during air travel
Ear wax
მეტი პაციენტის ბროშურებიშედით სისტემაში ან გამოიწერეთ BMJ Best Practice
ამ მასალის გამოყენება ექვემდებარება ჩვენს განცხადებას