Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- stridor
- onset within 2 weeks of birth
- features of airway obstruction
- resolution of symptoms by 2 years of age
- normal cry
Other diagnostic factors
- feeding difficulties
- weight loss or failure to thrive
- hypotonia
- dysmorphic features
Risk factors
- GORD
- neurological abnormalities
- laryngeal anatomical abnormalities
- male sex
- genetic syndromic disorder
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- flexible laryngoscopy
Investigations to consider
- rigid laryngobronchoscopy
- FEES testing
- polysomnography
- chest x-ray
- lateral neck radiograph
- ECG
- echocardiogram
Treatment algorithm
mild disease
moderate disease
severe disease
Contributors
Authors
Simone J. Boardman, MBBS, FRACS (OHNS)
Consultant Paediatric Otolaryngologist
The Children's Hospital at Westmead
Sydney
Australia
Disclosures
SJB declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Simone Boardman would like to gratefully acknowledge Mr C. Martin Bailey, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
CMB is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Kevin Pereira, MD
Director
Pediatric Otolaryngology-HNS
University of Maryland School of Medicine
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
KP declares that he has no competing interests.
Haytham Kubba, FRCS
Consultant Paediatric Otolaryngologist
Royal Hospital for Sick Children (Yorkhill)
Glasgow
UK
Disclosures
HK declares that he has no competing interests.
Gresham Richter, MD
Assistant Professor
Associate Residency Program Director
Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
Little Rock
AR
Disclosures
GR declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Olney DR, Greinwald JH Jr, Smith RJ, et al. Laryngomalacia and its treatment. Laryngoscope. 1999 Nov;109(11):1770-5. Abstract
Carter J, Rahbar R, Brigger M, et al. International Pediatric ORL Group (IPOG) laryngomalacia consensus recommendations. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Jul;86:256-61. Abstract
McCaffer C, Blackmore K, Flood LM. Laryngomalacia: is there an evidence base for management? J Laryngol Otol. 2017 Nov;131(11):946-54. Abstract
Yellon RF, Goldberg H. Update on gastroesophageal reflux disease in pediatric airway disorders. Am J Med. 2001 Dec 3;111(suppl 8A):78S-84S. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
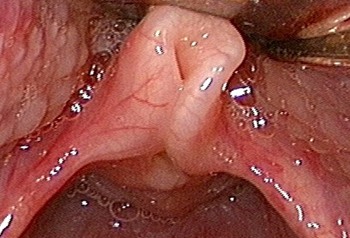
Differentials
- Vocal cord palsy
- Subglottic stenosis
- Laryngeal web
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Laryngomalacia consensus recommendations
- New Zealand guidelines for the assessment of sleep-disordered breathing in childhood
More GuidelinesPatient information
Reflux in infants
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer