Summary
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
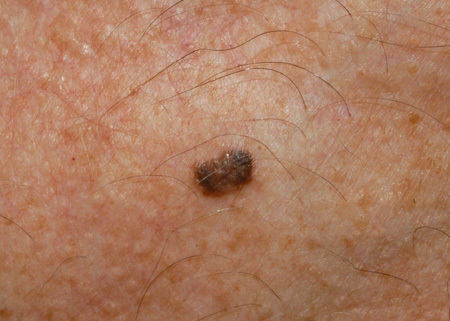
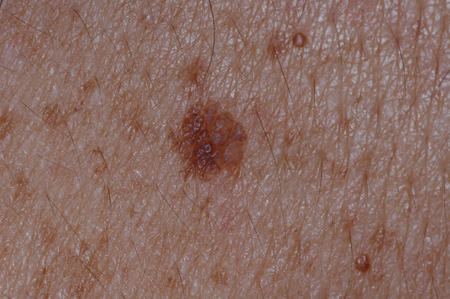
- lesions appear "stuck-on"
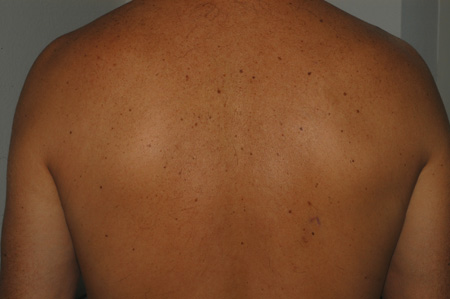
- localization on torso or face
- yellow or light- to dark-brown-colored lesions
- slightly raised, flat surface lesions
- wart-like texture
- multiple lesions
- painless
- itching (prurigo)
Outros fatores diagnósticos
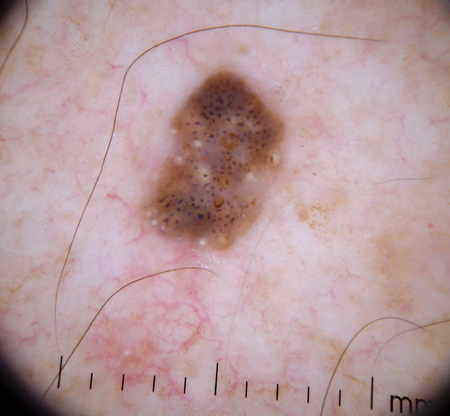
- round yellow-white horn pearls in the surface of lesions
Fatores de risco
- age over 50 years
- Fitzpatrick skin type I or II
- Fitzpatrick skin type IV, V, or VI (dermatosis papulosa nigra)
- female sex (dermatosis papulosa nigra)
- family history
- sun/UV exposure
- pregnancy
Investigações diagnósticas
Investigações a serem consideradas
- dermoscopy
- biopsy and histopathologic examination
- reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM)
Algoritmo de tratamento
irritated or itching lesions
raised seborrheic keratosis
flat seborrheic keratosis
Colaboradores
Autores
Ralph Braun, MD
Professor
Clinic Utoquai
Zurich
Switzerland
Declarações
RB declares that he has no competing interests.
Isabel Kolm-Djamei, MD
Consultant Dermatologist
Department of Pathology
Cantonal Hospital Lucerne
Lucerne
Switzerland
Declarações
IKD declares that she has no competing interests.
Revisores
Erin Warshaw, MD, MS
Associate Professor
Department of Dermatology
University of Minnesota
MN
Declarações
EW declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Seaton E, Madan V. Benign keratinocytic acanthomas and proliferations. In: Barker J, Griffiths C, Bleiker T, eds. Rook's textbook of dermatology. 10th ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2024.
Patterson JW. Chapter 32: Tumors of the epidermis. In: Patterson JW. Weedon's skin pathology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025: 877-936.
Barthelmann S, Butsch F, Lang BM, et al. Seborrheic keratosis. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2023 Mar;21(3):265-77.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.

Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Malignant melanoma
- Viral warts
- Nevus
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal