小结
定义
病史和体格检查
关键诊断因素
- chest pain
- dyspnea
- hyperexpanded ipsilateral hemithorax
- hyper-resonant ipsilateral hemithorax
- ipsilateral absent or diminished breath sounds
- extreme breathlessness
- trachea shifted to contralateral side
危险因素
- cigarette smoking
- family history of pneumothorax
- tall and slender body build
- age <40 years
- recent invasive medical procedure
- chest trauma
- acute severe asthma
- COPD
- tuberculosis
- AIDS-related Pneumocystis jirovecii infection
- cystic fibrosis
- lymphangioleiomyomatosis
- Marfan syndrome
- homocystinuria
- primary lung cancer and metastatic cancer to the lungs
- Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome
- pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis
- Erdheim-Chester disease
诊断性检查
首要检查
- chest x-ray
- chest ultrasound
需考虑的检查
- CT chest
- bronchoscopy
治疗流程
tension pneumothorax
primary spontaneous pneumothorax AND patient ≤ 50 years old
secondary spontaneous pneumothorax OR patient > 50 years old
traumatic pneumothorax
pneumothorax ex vacuo
catamenial pneumothorax
撰稿人
作者
Christopher Kapp, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine, Interventional Pulmonologist
Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care, Section of Interventional Pulmonary
Northwestern Memorial Hospital
Chicago
IL
Disclosures
CK declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Christopher Kapp would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Lonny Yarmus, Dr Jason Akulian, Dr Ryland P. Byrd Jr, Dr Thomas M. Roy, and Dr Anita Alwani, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
LY, JA, RPB, TMR, and AA declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Marc Noppen, MD
Professor and Chief Executive Officer of Respiratory Division
Interventional Endoscopy Clinic
University Hospital Brussels
Brussels
Belgium
Disclosures
MN declares that he has no competing interests.
Steve A. Sahn, MD
Professor of Medicine
Division of Pulmonary Critical Care, Allergy and Sleep Medicine
Medical University of South Carolina
Charleston
SC
Disclosures
SAS declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
British Thoracic Society. Guidelines: pleural disease. Jul 2023 [internet publication].Full text
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: intensive care unit patients. 2020 [internet publication].Full text
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: rib fractures. 2018 [internet publication].Full text
British Thoracic Society. Clinical statements: pleural procedures. Jul 2023 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
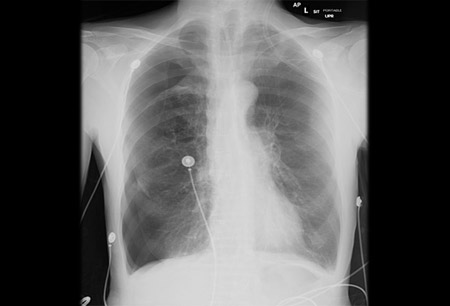
Differentials
- Asthma, acute exacerbation
- COPD, acute exacerbation
- Pulmonary embolism
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- BTS Guidelines on Pleural Disease
- ACR appropriateness criteria: intensive care unit patients
More GuidelinesPatient information
Pneumothorax
Chest drain insertion
More Patient informationVideos
Needle decompression of tension pneumothorax: animated demonstration
Insertion of intercostal drain, Seldinger technique: animated demonstration
More videosLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer